
PESTLE & MORTAR 3 October 2024
This Week:
EvilCorp and Cybersecurity
Israel, Iran, and War
Port Workers Strike Threatens Global Economy
Japan’s New Prime Minister Could Shift Foreign Policy
Islamic State Doubles in Size in Somalia
Hurricane Helene’s Impact on Semiconductors
Eurozone Inflation Falls, ECB Rate Cut Likely
Austrian Right-Wing Victory
EvilCorp and Cybersecurity
The UK’s National Crime Agency (NCA) has revealed that the Russian cybercriminal group Evil Corp has close ties with the Russian state, specifically its domestic spy agency, the FSB. Evil Corp carried out cyber-attacks against NATO countries, supported by these connections. In addition, Evil Corp has been responsible for numerous cyberattacks, including using banking trojans like GameOverZeus and Dridex to steal hundreds of millions of dollars globally. When the U.S. imposed sanctions and indicted members in 2019, Evil Corp's leader, Maksim Yakubets, turned to his father-in-law, former FSB official Eduard Benderskiy, for protection. Evil Corp operates like a traditional crime family, involving Yakubets' relatives, and has evolved its tactics since facing legal pressure. The group has developed new ransomware and partnered with Russian gang LockBit, which runs ransomware-as-a-service. Despite a crackdown on LockBit’s operations, the NCA believes some attacks may continue, though LockBit may be overstating its activity to downplay the crackdown’s impact.
Eduard Benderskiy, a former Russian intelligence officer, has been sanctioned by Western authorities for his role as a key enabler and protector of the Evil Corp cybercrime group. Benderskiy used his influence to shield the group from Russian authorities, especially after sanctions were imposed in 2019. Furthermore, Benderskiy’s ties to Russia’s intelligence services facilitated Evil Corp’s operations, which included espionage against NATO countries. Although no longer formally associated with the security apparatus, Benderskiy has been linked to Russia’s FSB through his past roles in elite KGB units. He continues to maintain strong Kremlin connections and operates both a security company and a charity linked to Russia’s intelligence services.
Western authorities have also named Russian national Aleksandr Ryzhenkov as a key member of the Evil Corp cybercrime group and a LockBit ransomware affiliate. The U.S. charged Ryzhenkov with using BitPaymer ransomware to extort U.S. businesses. This announcement is part of a broader crackdown on LockBit, which has seen multiple arrests, including suspected money launderers in the UK, a developer in France, and a "bulletproof hosting" company owner in Spain. Although LockBit’s platform continues to operate, law enforcement actions have significantly reduced its capacity. The group’s remaining activity includes reposting old compromises and making fake or misattributed claims. A previous operation by the UK’s National Crime Agency (NCA) gained extensive access to LockBit’s systems, revealing that the group often retained victim data despite promises to delete it.
Such nation-state sponsored groups are not new, but this provides evidence of how Russian APTs operate. Though Russia often looks the other way concerning criminal gangs, as long as they do not do attack in the homeland, the connection with former a former intelligence operator shows a more direct connection. When Western powers and companies are assessing such APTs, investigations like from the UK can provide insight into structure, TTPs, targeting, and overall capabilities of these groups.
Israel, Iran, and War
Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) launched a significant missile attack on Israel, reportedly to avenge the deaths of key allies: Hamas leader Ismail Haniyeh, Hezbollah leader Hassan Nasrallah, and IRGC commander Abbas Nilforoushan, who were killed in Israeli strikes. Iran claimed the attack targeted Israeli military and intelligence sites with around 200 ballistic missiles, including hypersonic ones. Israel, with U.S. support, intercepted most missiles but confirmed a few hits. Iran warned that future retaliation would be more forceful if Israel responds, yet Israel vowed to strike back. The U.S. signaled support for Israel, raising the potential for broader regional conflict, but the Biden administration is unlikely to take strong measures to do so.
This attack is unlikely to signal a broader war between Israel and Iran. While Iran felt compelled to retaliate for the death of an ally, it is highly probable that they provided advance warning to Israel, the U.S., and others. The U.S. had enough foreknowledge to allow Jordan and Israel to prepare their missile defenses. This scenario mirrors events in April, with these ballistic missile strikes more aimed at signaling to domestic audiences than escalating conflict. Iranian leadership needs to demonstrate a response to domestic pressures but is still unlikely to pursue a direct confrontation or war with Israel. Nasrallah was less significant to Iran than Qasem Soleimani, and Iran did not go to war with the U.S. after Soleimani's neutralization.
However, Israel is expected to expand its operations in Lebanon following Nasrallah's death. The IDF has essentially neutralized Hezbollah’s political and military leadership and likely sees this as an opportunity to degrade the group further. Israel is highly likely to intensify efforts to target Hezbollah’s offensive capabilities, particularly its precision-guided missiles and infrastructure in southern Lebanon, with continued military action anticipated in the coming months. Hezbollah, in turn, is likely to take greater risks, possibly attempting kidnappings of Israeli soldiers, which could prompt increased Israeli military responses. When groups like Hezbollah lose their leadership, they often become more violent under less experienced command, becoming more aggressive but less organized and effective. Politically, Hezbollah’s dominance in Lebanon may weaken, providing an opening for opposing factions to regain influence as the group struggles to reorganize.
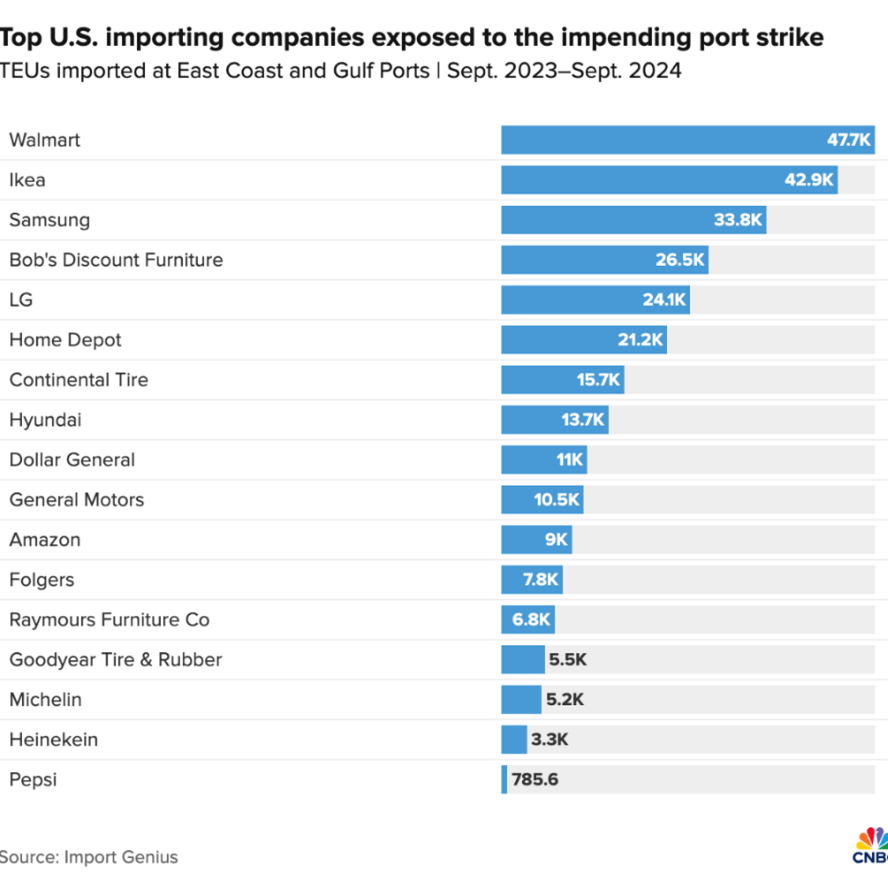
Port Workers Strike Threatens Global Economy
Port workers on the East Coast of the United States have started a strike during their labor negotiations, and this strike has the potential to devastate the U.S. economy. The Biden administration has sided with the striking workers despite the threat to the economy, and they are pressuring U.S. port employers to increase their offer to resolve a strike by the International Longshoremen's Association (ILA), which is disrupting half of the country's ocean shipping. The strike has halted the movement of goods from food to automobiles across 36 ports from Maine to Texas, threatening to cost the U.S. economy billions daily. Over 38 container ships are already backed up, compared to just three before the strike. The ILA, representing 45,000 dockworkers, is demanding higher wages and protections against port automation after rejecting a 50% wage hike offer from the United States Maritime Alliance (USMX).
Biden has criticized foreign ocean carriers for making profits during the pandemic while dockworkers risked their health, urging carriers to offer a fair contract. Meanwhile, economists warn that the strike could raise inflation and impact growth if prolonged because of the severe negative impacts to the global supply chain. European automakers are most at risk from the strike, and a longer walkout could actually debilitate the sector. Retailers are implementing backup plans to mitigate the disruption ahead of the holiday season, while shipping stocks, such as Maersk and ZIM Integrated Shipping, have seen declines. Businesses reliant on ocean shipping are concerned, as U.S. waterways handle half of imports and 37% of exports. The National Retail Federation and some Republicans are urging Biden to use federal authority to halt the strike, but Biden has so far resisted. However, the U.S. Department of Agriculture does not foresee significant changes to food prices or availability in the short term. See here for research from CSIS on the geopolitics of port security.
Japan’s New Prime Minister Could Shift Foreign Policy
At his first press conference, Japan's new prime minister, Shigeru Ishiba, stated that the “security environment surrounding our country is the most severe since the end of World War II.” Ishiba was previously a defense minister known for promoting an Asian NATO to counter China’s hegemonic pursuits and North Korean Missiles. In addition, Ishiba stated, "With the Japan-US alliance as a foundation, we will expand the circle of friendly and like-minded countries, using diplomacy and defense to realize the peace of Japan and the region.” He has previously called for the creation of an Asian NATO to counter China's rapid military build-up, North Korean missile launches and other security threats. The former prime minister Shinzo Abe tried to build up Japan’s military prowess and geopolitical position, but the situation has worsened since he left office. If Ishiba is successful, then Japan will offer an important contribution to containing China and creating a balance of power in the region. A key indicator that Japan will move in that direction will be the results of the snap election on October 27. While the LDP is expected to win, by how much will show the political capital Ishiba will have to pursue this change in foreign policy.
Islamic State Doubles in Size in Somalia
The Islamic State in Somalia has doubled in size over the past year, according to U.S. Africa Command (AFRICOM) commander Gen. Michael Langley. Although the exact number of fighters is not disclosed, earlier estimates placed it around 200. This growth raises concerns about an increase in foreign fighters and potential links to other extremist groups. Al-Shabab, another major militant group, has continued its recruitment and financing efforts, capitalizing on political disputes between Somalia and Ethiopia. The group's numbers are estimated between 12,000 and 13,000 fighters. Al-Shabab has maintained a strong presence despite military efforts to clear territories in Somalia, carrying out deadly attacks in Mogadishu and other regions. Somalia also faces threats from Iranian-backed Houthi militants in Yemen, who may seek to collaborate with al-Shabab, potentially destabilizing the region further by targeting key maritime routes. The upcoming African Union Transition Mission in Somalia will be replaced by a new stabilization mission in 2025, with details yet to be finalized. This is a strong indicator of the increase in Islamist terrorist in the medium term, and that will highly likely have a destabilizing impact in Africa.
Hurricane Helene’s Impact on Semiconductors
Spruce Pine, a small town in the Blue Ridge Mountains, is home to some of the purest quartz on Earth, which is crucial for global microchip production. This quartz, essential for manufacturing advanced microchips, particularly in the creation of high-purity silicon, has made the town a key player in the semiconductor supply chain. However, the recent Hurricane Helene caused severe flooding, shutting down the mines indefinitely and threatening global chip production. Spruce Pine quartz is unique due to its high-purity and minimal contaminants, making it more affordable and essential for the chip industry. Around 70% of the quartz used in advanced chips comes from Spruce Pine. While there are other quartz sources, they are less pure and more expensive to refine. The closure of the mines may disrupt the already fragile chip supply chain, as demand for advanced chips is expected to surge by 30% by 2026 due to AI growth. Though chipmakers may have stockpiles of polysilicon, the long-term effects could lead to higher prices for electronics and increased environmental costs from sourcing quartz elsewhere. The situation highlights the vulnerability of global supply chains, often reliant on a single small town for critical materials.
Eurozone Inflation Falls, ECB Rate Cut Likely
Eurozone inflation fell to 1.8% in September, dropping below 2% for the first time since mid-2021, driven mainly by lower energy costs and muted goods prices. Core inflation, which excludes volatile items like energy, dipped slightly to 2.7%. This decline strengthens the case for a European Central Bank (ECB) rate cut in October, as inflation continues to ease and growth data weakens. ECB President Christine Lagarde has signaled the likelihood of a rate cut, with markets now pricing in an 85% chance of this happening. The ECB may continue cutting rates into December and January, as inflation trends remain below projections, leading to increased expectations for further easing.
Austrian Right-Wing Victory
Austria's right-wing Freedom Party (FPO) won its first-ever parliamentary election, capturing around 29% of the vote. However, despite this victory, the FPO faces challenges in forming a governing coalition, as most other parties have dismissed its overtures. The party’s leader, Herbert Kickl, known for his controversial views and alliance with Hungary's Viktor Orban, has struggled to gain support from mainstream parties. The FPO's success is part of the broader rise of far-right parties across Europe, though this often doesn't guarantee political power due to resistance from other political groups. Kickl’s policies, including opposition to sanctions on Russia and a hard stance on immigration, resonate with voters concerned about inflation and national identity. However, critics worry about the potential "Orbanisation" of Austria, fearing a drift toward authoritarianism. If Kickl is unable to form a coalition, it could lead to a partnership between Austria's traditional center-right and center-left parties. Importantly, this is another indicator of the rise of nationalism in Europe as several countries now have strong minorities of right-wing and nationalist parties winning electoral representation.
"In any given moment, we have two options: to step forward into growth or to step back into safety.”
- Abraham Maslow
If you enjoyed this newsletter why not sign up to receive it by email